
|
Международное совещание
|
Участники и доклады
The future next-generation neutrino telescope Baikal-GVD will be a km3-scale
array aimed at detection of astrophysical neutrino fluxes.
It will have a modular structure and consist of functionally independent sub-arrays –
clusters of strings of optical modules. The prototyping phase of
the project has been completed in 2015 with deployment of the first cluster
of Baikal-GVD in the Lake Baikal. We discuss current status and prospects
of the Baikal-GVD project.
Streams of ultracold neutrons are used in experiments on measurement of the dipole moment
of the neutron, and to test the hypothesis of the existence of neutron-antineutron
oscillations with non-conservation of baryon quantum number ΔB = 2.
We tested the possibility of cooling and formation of thermal neutron flux
by a constructive neutron monitor NM - 64 [1] cooled by liquid nitrogen vapors.
For neutron detection in the installation may be used the scintillation method [2]
or proportional counters [3] . We also presented a helium cryostat for
cooling and formation of neutron fluxes. Calculations have been done
for cold neutron flux density by using a cascade generator and reaction t (d, n)
4He at a deuteron energy of 130 keV and for signal/background ratio for various
lengths of neutron-antineutron oscillations in
vacuumed vertically placed pipe with length L ≈ 10 m.
We estimate the energy reservoir available in the deconfinement phase transition
induced collapse of a neutron star to its hybrid star mass twin on the "third family"
branch, using a recent equation of state of dense matter.
The available energy corresponding to the mass-energy difference between configurations
is comparable with energies of the most violent astrophysical burst processes.
An observational outcome of such a dynamical transition might be fast radio bursts,
specifically a recent example of a FRB with a double-peak structure in its light curve.
Представлены результаты поиска совпадений редких событий на детекторах LVD и
Баксанского подземного сцинтилляционного телескопа (БПСТ). Разработана методика поиска событий
в детекторах LVD и БПСТ, которые могли быть вызваны взаимодействием нейтрино с веществом,
входящим в их состав. Показано, что с 2011 по 2014 годы совпадения носят случайный характер
и их суммарное количество за год остаётся практически неизменным.
Core-collapse of massive stars produces both neutrino signal
and gravitational wave (tensor-transversal plus scalar-longitudinal) bursts.
In the case of GW detectors having low angular resolution the method of
sidereal time analysis of output signals was applied for extraction of GW-bursts
from high level noise. This method was suggested by J.Weber, Phys. Rev. Letters
22, 1320, 1969 for signal analysis of his bar detector and developed
for the case of existing GW detectors in papers by Y.Baryshev and G.Paturel,
A&A, 371, 378, 2001 (arXiv: astro-ph/0104115), P.Astone et al., CQG,
19,5449, 2002 (arXiv: gr-qc/0210053), G.Paturel and Y.Baryshev,
A&A, 398, 377, 2003 (arXiv: astro-ph/0104115), G.Paturel and Y.Baryshev,
ApJ Lett., 592, L99, 2003.
The same sidereal time approach can be also applied for low energy neutrino detectors having many years of observational time (e.g. Super-Kamiokande, LVD, Baksan). This method uses following basic things: 1) difference between sidereal and mean solar time (which help to delete noises related to day-night solar time), 2) directivity diagram (antenna pattern) of the detector (which chooses a particular sky region in particular sidereal time), and 3) known position on the sky the inhomogeneous distribution of the possible sources of SN signals, such as Galactic plane, Galaxy center, closest galaxies, Virgo galaxy cluster, Super-galactic plane, Great Attractor. Main idea is calculation of the expected number of neutrino events as a function of sidereal time (scanning the sky by Earth rotation) produced by possible sources within fixed depth of the survey. The summation of all output signals within one Earth’s revolution (∼23h 56m 04s of mean solar day) during several years of observations will reveal certain structure at predicted sidereal hours (by using directivity pattern of a detector), so the detection has statistical sense.
Recycling scenario imposes important constraints on r-mode instability in neutron stars
and thus on neutron star microphysics. Recent Ref. [1] concluded that
ungapped interacting quark matter model is consistent with recycling scenario,
including radio and x-ray data. However, this model leads to very high neutrino
luminosity, thus high temperatures observed for neutron stars in low mass X-ray
binaries can hardly be explained. On the contrary, our recent model [2] agrees
with these observations, furthermore it is also consistent with neutron star cooling data,
because it appeals to the same microphysical parameters as the minimal cooling model does [3].
Within our model, r-mode instability is suppressed because of the resonant interaction
of oscillation modes at some internal temperatures ("resonant temperatures").
Here we demonstrate that this model agrees as well with observations of millisecond pulsars
and provides observational evidences that the coupling parameter for resonant mode interaction
at low temperatures should be rather large, in agreement with theoretical expectations [2].
This study was partially supported by RFBR (grants 14-02-00868-a and 14-02- 31616-mol-a), and by RF president programme (grants MK-506.2014.2 and NSh-294.2014.2). References [1] M.G. Alford and K. Schwenzer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 251102 (2014). [2] M.E. Gusakov, A.I. Chugunov, and E.M. Kantor, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 151101 (2014); Phys. Rev. D 90, 063001 (2014). [3] M.E. Gusakov et al, A&A 423, 1063 (2004); Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 363, 555 (2005).
We present spectral and timing analyses of the X-ray emission from the pulsar wind nebula DA 495
and its central object, J1952.2+2925, suggested to be the pulsar, using archival Chandra and
XMM–Newton data. J1952.2+2925 has a pure thermal spectrum which is equally well fitted either
by the blackbody model with a temperature of 215 eV and an emitting area radius of 0.6?km or
by magnetized neutron star atmosphere models with temperatures of 80–90 eV.
In the latter case, the thermal emission can come from the entire neutron star surface
which temperature is consistent with standard neutron star cooling scenarios.
We place also an upper limit on the J1952.2+2925 non-thermal flux.
The derived spectral parameters are generally compatible with published ones based only
on the Chandra data, but they are much more accurate due to the inclusion of XMM–Newton data.
No pulsations were found and we placed an upper limit for the J1952.2+2925
pulsed emission fraction of 40 per cent. Utilizing the interstellar absorption–distance
relation, we estimated the distance to DA 495, which can be as large as 5 kpc
if J1952.2+2925 emission is described by the atmosphere models. We compiled possible
multiwavelength spectra of the nebula including radio data; they depend on
the spectral model of the central object. Comparing the results with other pulsar
plus wind nebula systems, we set reasonable constraints on the J1952.2+2925
spin-down luminosity and age. We suggest that the Fermi source 3FGL J1951.6+2926 is
the likely gamma-ray counterpart of J1952.2+2925.
We perform the analysis of a data set of Baikal neutrino telescope
NT200 to search for neutrino signals from dark matter annihilation
in the Galactic Center and in Dwarf Galaxies. From this analysis
we set upper limits on dark matter annihilation cross sections for
different annihilation channels. Also we discuss sensitivity of the
gigaton volume telescope Baikal-GVD to this signal.
I will review the two-families scenario in which hadronic stars having rather small radii and masses
not exceeding about 1.5 Ms coexist with quark stars, which can reach masses well above 2 Ms.
I will discuss the implications of this scenario in particular for long and short GRBs, using the results
of our recent work in which the process of quark deconfinement in compact stars has been revisited.
Bibliographical references: 1) "Can very compact and very massive neutron stars both exist?" by Alessandro Drago, Andrea Lavagno, Giuseppe Pagliara. Phys.Rev. D89 (2014) 4, 043014. 2) "Early appearance of Δ isobars in neutron stars" by Alessandro Drago, Andrea Lavagno, Giuseppe Pagliara, Daniele Pigato. Phys.Rev. C90 (2014) 6, 065809. 3) "Combustion of a hadronic star into a quark star: the turbulent and the diffusive regimes" by Alessandro Drago, Giuseppe Pagliara. arXiv:1506.08337 4) "Quark deconfinement and the duration of short Gamma Ray Bursts" by Alessandro Drago, Andrea Lavagno, Giuseppe Pagliara In preparation
We analyze Carpet-2 EAS array data in order to search for events with
anomalously low content of muons with energies Eμ > 1 GeV in extensive
air showers with energy above 100 TeV. Monte-Carlo simulations of showers
induced by primary protons and gammas have been performed using the CORSIKA code.
The estimation of the upper limit on the flux primary gamma rays is presented.
Radiochemical neutrino detectors have played an important role in the study
of neutrinos from the Sun. Features of radiochemical detectors - no external
backgrounds and sensitivity only to electron neutrinos - make them
a powerful tool for precision measurements of neutrino properties
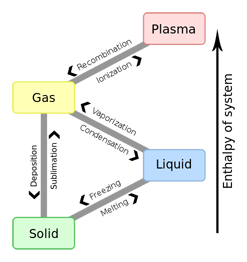
Features of Gas-Liquid (GL) and Quark-Hadron (QH) phase transitions (PT) in dense nuclear matter
are under discussion in comparison with their terrestrial counterparts, e.g. so-called "plasma"
PT in shock-compressed hydrogen, nitrogen, xenon etc. Both, GLPT and QHPT, when being represented in
widely accepted temperature–baryonic chemical potential plane, are often considered as similar, i.e. amenable
to one-to-one mapping by simple scaling. It is argued that this impression is illusive and that GLPT and QHPT
belong to different classes: GLPT is typical enthalpic (e.g. Van-der-Waals-like) PT while QHPT
(i.e. "deconfinement-driven" PT) is typical entropic PT. Subdivision of 1st-order
fluid-fluid phase transitions into two subclasses: enthalpic and entropic PTs (i.e. H-PT and S-PT),
was proposed in [arXiv:1403.8053/1504.05850]. The term "entropic PT" is not equivalent to the term
"entropy-driven" PT, which was introduced previously by D. Frenkel. We clarify the difference of two types of PTs.
Properties of H-PT and S-PT differ significantly. Entropic PT is always internal part of
more general and more extended thermodynamic anomaly – domains with abnormal (negative) sign for the set
of (usually positive) second cross derivatives of thermodynamic potential. Three of them are of primary importance:
so-called Gruneizen coefficient, thermal expansion coefficient and thermal pressure coefficient. Negative sign of all that derivatives
lead to violation of relative order and standard behavior in P–V plane for many iso-lines, e.g. isotherms,
isentropes, shock adiabats etc. Entropic PTs have more complicated topology of stable and metastable domains
within the two-phase region in comparison with conventional enthalpic (VdW-like) PTs. In particular, new additional
(third) metastable region, bounded by new additional spinodal, appears in the case of entropic PT.
All the features of entropic PTs and accompanying abnormal thermodynamics region have transparent geometrical
interpretation -- multi-layered structure of thermodynamic surfaces for temperature, entropy and internal energy
as a pressure-volume functions, e.g. for T(P,V), S(P,V) and U(P,V).
Here we briefly summarize our long period experience of constructing and
operating wide-field monitoring cameras with sub-second temporal resolution
to look for optical components of GRBs, other rapid astrophysical phenomena,
fast-moving satellites and meteors. General requirements for hardware
for such systems are discussed along with algorithms of real-time detection
and classification of various kinds of short optical transients.
We also give a status report on the next generation, multi-objective and
transforming monitoring system, the MegaTORTORA, whose 9-channel prototype
(MiniMegaTORTORA) is now in operation at Russian Special Astrophysical Observatory.
This system combines a wide field of view with subsecond temporal resolution
in monitoring regime, and is able to reconfigure itself, in a fractions of second,
to follow-up mode which has better sensitivity and provides us with multi-color
and polarimetric information on detected transients simultaneously.
We discuss first results of its work, as well as its prospects.
In present the interest to nuclear matter hydrodynamics increases [1].
The Liquid Drop Model (LDM) is successfully used for semi-empirical formulation
of surface and Coulomb terms in Bethe-Weizsacker mass formula.
LDM is the foundation for the 5D harmonic oscillator collective nuclear model [2],
which allows us interpreting vibration excitations of near-spherical nuclei.
In the frame of nuclear liquid drop model an analytical solution for the frequency
of capillary oscillations is obtained with taking into account the damping
due to viscosity and surrounding medium polarizability. The model has been applied
for estimation of even-even spherical nuclei surface tension and viscosity.
It has been shown [3] that energy shift of capillary oscillations of even-even
spherical nuclei due to viscous dissipation gives viscosities in the interval
4.2-7.6 MeV fm-2 c-1 for nuclei from Pd–106 to Hg–198.
For non-zero temperatures the ratio of shear viscosity η to entropy density
s is estimated and compared with the limit η/s > 1/4π
motivated by AdS/CFT for quark–gluon plasma [4].
Early discovery of an optical afterglow of the gamma-ray burst GRB140801A in the 137°
(3-σ error-box) of the Fermi Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM). GRB140801A is one of the few GRBs
whose optical counterpart was discovered solely from its GBM localization. The optical afterglow
of GRB140801A was found by the MASTER Global Robotic Net 53 sec after receiving the alert,
making it the fastest optical detection of a GRB from a GBM error-box. Spectroscopy obtained
with the 10.4-m Gran Telescopio Canarias and the 6-m BTA of SAO RAS reveals a redshift of z=1.32.
We performed optical and near-infrared photometry of GRB140801A using different telescopes
with apertures ranging from 0.4-m to 10.4-m. GRB 140801A is a typical burst in many ways.
The rest-frame bolometric isotropic energy release and peak energy of the burst is
Eiso = 5.54-0.24+0.26 × 1052 erg
and Ep, rest≅280 keV, respectively, which is consistent with the Amati relation.
The absence of a jet break in the optical light curve provides a lower limit on the
half-opening angle of the jet θ=6.1°. The observed Epeak is consistent
with the limit derived from the Ghirlanda relation. The joint Fermi GBM and Konus-Wind analysis
shows that GRB140801A could belong to the class of intermediate duration. The rapid detection
of the optical counterpart of GRB140801A is especially important regarding the upcoming experiments
with large coordinate error-box areas.
An overall view of the Baksan Neutrino Observatory of the INR RAS infrastructure is presented.
Ground-based and underground facilities used to study cosmic rays, rare nuclear reactions and
decays, register solar neutrino, observe various geophysical phenomena are described.
Some main results obtained with these facilities and prospects are given.
Recently, the Crab Nebula, once a "standard candle" of X-ray and
gamma-ray astronomies, was shown by satellite gamma-ray telescopes Fermi-LAT
and AGILE to produce flares of gamma-rays in the energy range around 100 MeV.
However, as long ago as more than 20 years from now the data on a possible burst
in the Crab Nebula at much higher energies, about 100 TeV, were published.
Characteristics of transient and stationary fluxes of gamma rays from
the Crab Nebula in various energy ranges are compared to discuss whether
the old data obtained at ultra-high energy could be reasonably consistent
with the modern pattern of burst activity of the source.
The MASTER Global Robotic Net is the unique modern Russian experiment in astrophysics.
MASTER is a both alert and survey telescope with its own developed software, which allows us discovering new optical transients in MASTER images within several minutes after readout from CCD. This information includes the full classification of all sources from an image, the data from previous MASTER-Net archive images for every source, full information from VIZIER database and all open sources, derivation of orbital elements for moving objects, etc. This software permitted us discovering more than 900 optical transients of more than 10 types within recent years. The MASTER Global Robotic Net includes observatories at 3 continents and in the Atlantic ocean. All MASTER observatories are equipped by identical instruments with identical photometers with BVRI filters and polarizers. Each MASTER observatory provides a survey speed of 128 deg2 per hour with a limiting magnitude of 20 mag at dark moonless nights (a wide field optical channel) and 800 square degrees per 1 second up to 12m (a very wide field optical channel). These features allow us observing fields of view of FERMI (error-boxes of up to tens of square degrees), Swift, ANTARES, IceCube, LIGO/VIRGO in the alert mode and discovering optical transients in real-time.
The mechanisms of explosion of different type supernovae (SNe) are discussed.
At least three mechanisms are under detailed inspection of scientific community for core collapse SNe.
They are the instability of standing accreting shock front that results
in the large scale 3-dimensional hydrodynamic flows, the magnetic-rotational expulsion
of supernova envelope, and rotational fission of collapsing stellar core into
a pair of proto neutron stas. The mechanism of explosion of cosmological SNe (of Type Ia)
is physically understood as thermonuclear explosion of carbon-oxygen-helium matter.
However there exists serious problem with modelling of the structure and propagation
of unstable thermonuclear flame that is crusial for numerical agreement with observations.
The current status of the experiment on recording neutrino bursts from core collapse
stars is presented. The actual observational time is 29.76 years. The upper bound
of the mean frequency of core collapse supernovae in our Galaxy is
fcol < 0.077 year-1 (90% CL).
The first results of joint analysis of experimental data on the search
for neutrino bursts using the BUST and LVD detectors are presented.
We carried out a search for the coincidence of events in both facilities (BUST and LVD)
using data for 2011- 2014 years. The obtained results can be explained
by random coincidence of background events in LVD and BUST.
The presented analysis of data of two and more facilities can be particularly
useful in cases when optical SN is invisible for various reasons.
The QCD phase transition during the postbounce evolution of core-collapse supernovae
can be observable as the second peak in the neutrino signal that is accompanied
by significant changes in the energy of the emitted neutrinos. In contrast
to the first neutronization burst, this second neutrino burst is dominated
by the emission of antineutrinos. This circumstance is useful for detection
of this peak due to the high cross section of inverse beta decay reaction.
Because the supernova explosion in the Galaxy is a rare event; the comprehensive study of the next one has absolute priority for the low-energy neutrino astronomy. Therefore the new-generation large liquid scintillation detectors must be ready to detect all flavors of neutrinos in order to understand the physics and astrophysics of core-collapse supernovae. For this purpose the new detector must have the capability to distinguish the various detection channels. Large statistics must be collected to study spectra and time profiles of all neutrino flavors, thereto the new detector should have large enough target mass. The prospects for detecting the peculiarities in the neutrino signal from the core-collapse supernova in large liquid scintillation detectors will be discussed.
A brief review of present situation in development of GW detector technique is described.
Current upper limits of GW radiation from main classes of relativistic astrophysical objects
are given. Strategy of multichannel search for so called "multi messenger astronomy"
is discussed. It is associated with the properties of three types of transient
astrophysical sources that are well known in the EM spectrum.
These sources are expected to produce transient GW signals in the laser interferometric
detector frequency range, and possibly neutrino fluxes as well.
In that number there are 1) coalescence of NS and BH binary systems,
2) core collapsing stars, 3) flaring/bursting NSs.
Joint GW+EM and neutrino observations are expected to provide a wealth of information
among which: a) improvement in the confidence in first GW detection,
b) useful priors in GW data analysis parameter space,
c) complement our knowledge of the physics of sources.
Algorithms of joint multichannel data processing are under development.
Past results from MM searches show no significant coincident events,
and obtained upper limits on the energetics in GW and source rate density
did not provide strong constraints on astrophysical models.
However for the advanced detectors, starting from 2018 year probed distances
are expected to contain significant number of GW sources localized
in few degrees areas in the sky and the more than ten MoU partners
will ensure EM and neutrino monitoring.
Исследуется взаимодействие потока электронных нейтрино возникающего в механизме ротационного сжатия
на первом этапе взрыва Сверхновой звезды с составляющими элементами детектора LSD – железом-56,
большая масса которого входит в конструкцию в качестве защиты, и жидким сцинтиллятором
СnH
The project is based on a cluster of telescopes for the wide monitoring of the celestial sphere.
The project is aimed at the following goals:
Astrophysical sources of information about distant objects in the Universe may be:
primary protons, gamma rays and neutrinos. But at energies greater than a few TeV photons interact
with infrared and microwave background. Protons and electrons due to their electric charge are affected
by magnetic fields in space and cannot allow us determining their trajectory from a source to the Earth.
Neutrinos have a very low cross section and provide us information about distant sources with negligible distortions - their direction remains almost unchanged. It distinguishes neutrinos from other elementary particles as the unique messengers. This fact is one of the most significant differences between neutrino detection and registration of photons and high-energy protons. Cherenkov radiation began to be in common use for detection of ultrahigh-energy neutrinos in the early 90-ies of the last century. The result was creation of a new class of systems — large volume deep-see neutrino telescopes. Since 2005 an MSU scientific group consisting of employees, graduate students and students of the Faculty of Physics and SINP participates in the work for designing, creation and data processing on the large volume neutrino telescopes in such projects as NEMO, ANTARES and KM3Net. Now main efforts of the scientific work conducted by the group are aimed at the following questions: -development and creation of new types of optical modules for photomultipliers on neutrino telescopes; -a new algorithm for finding supernovae and other astrophysical objects of this type using neutrino detection was developed; -the work for searching neutrinos from the recently discovered gamma-ray phenomena so-called "Fermi bubbles" which cause the luminescence in the galactic plane; -the work in modeling various configurations of optical modules for KM3Net(It) neutrino telescope; -the work on a possible acoustic detection of astrophysical neutrinos.
The origin of Ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULXs) in external galaxies
whose X-ray luminosities exceed those of the brightest black holes in
our Galaxy by hundreds and thousands of times is mysterious. The most
popular models for the ULXs involve either intermediate mass black
holes (IMBHs) with standard accretion disks or stellar-mass black holes
(~10 solar masses) accreting at super-Eddington rates. Here we review
the ULX properties, their X-ray spectra indicate presence of hot winds
in their accretion disks supposing the supercritical accretion. However,
the strongest evidences come from optical spectroscopy. The spectra of
the ULX counterparts are very similar to that of SS 433, the only known
supercritical accretor in our Galaxy.
There are two new observational facts: (1) the mass spectrum of neutron stars
and black hole candidates (or collapsars) shows an evident absence of compact objects
with masses within the interval from 2 M Sun (with a peak for neutron stars
at about 1.4 M Sun ) to approximately 6 M Sun,
(2) and in close binary stellar systems with a low-massive (about 0.6 M Sun)
optical companion the most probable mass value (the peak in the masses distribution
of black hole candidates) is close to 6.7 M Sun.
This puzzle of discrete mass spectra of compact objects demands some solution
in the context of the supernovae and gamma-ray bursts relation, and in connection
with the core-collapse supernovae explosion mechanism or, eventually, with QCD phase transition.
Particularly, the long gamma-ray burst can be one of the first signals
of core collapse of a massive star.
The clustering of galaxies around GRB sight-lines is detected and studied
in the same manner employed with quasar spectroscopy in many papers already.
Galaxies that give rise to absorption line systems in gamma-ray bursts afterglow spectra
have been directly imaged and investigated. So, it is possible to try to find
the overdensity excess of GRB field galaxies around GRB positions by different methods -
spectroscopic, photometric ones (deep images - multiband photometry) plus
the search for correlation with Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and others.
In this report we test for reliability any signatures of field galaxies clustering
in GRB 021004 line of sight.
(1) The first signature is the BTA and Hubble GRB 021004 field photometric redshift
distribution with the peak at z ∼ 0.57 estimated from multicolor photometry.
(2) The second signature is the MgII 2796,2803 absorption doublet at z ∼ 0.57
in GRB 021004 afterglow spectrum.
(3) The third signature is some inhomogeneity in Plank + GRB 021004 fields.
(4) And the fourth signature may be the galaxy clustering with
an effective redshift of z = 0.57 from the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS),
which is part of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey III (SDSS-III).
The discovery of astrophysical neutrinos has lifted a new observational window to the Universe.
A new generation of detectors aims to fully opening this window.
The talk will describe the corresponding IceCube results which herald a new era in neutrino astronomy.
It will also give an outlook to the future detectors on the multi-cubic kilometer scale:
KM3NeT in the Mediterranean Sea, GVD in Lake Baikal and IceCube-Gen2 at the South Pole.
We have studied the distribution of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) locations from the BATSE and BeppoSAX
space observatories relative to the cosmic microwave background (CMB) data by Planck space mission.
Three methods were applied for data analysis: (1) a histogram of CMB signal values in GRB directions, (2) mosaic correlation maps calculated for GRB locations and CMB distribution, (3) calculation of an average response (stacking procedure) in the area of "average GRB population" on the CMB map. A correlation between GRB locations and CMB fluctuations was detected which can be interpreted as the systematic effects in the process of observations. Besides, in the averaged areas of CMB maps, a difference between the distributions of average fluctuations for short and long GRBs was detected which can be caused by different natures of these events.
We present a review of instrument facilities of SAO RAS optical telescopes
– the 6-meter telescope BTA and the 1-meter telescope Zeiss-1000 aimed at the study
of transient phenomena in the Universe including those whose localization
in the celestial sphere is unknown in advance.
As a rule, the instruments for photometric and spectral investigation of such phenomena are parts of standard equipment of the telescopes and they can be used during most of their operational time. Results of the spectral and photometric study of optical afterglow of gamma-ray bursts fulfilled with the SAO RAS telescopes from 1998 are presented. One of the important tasks carried out in the framework of programs of collaboration with other national instruments is the synchronous monitoring of samples of active galactic nuclei in optical and radio. We adduce suggestions formulated in SAO RAS within the context of a program of scientific infrastructure development in the nearest 15-20 years and aimed at creation of survey instruments of medium size with the field of view of few degrees.
All known to date stellar mass black holes reside in X-ray binaries (XRB).
They are connected with a number of uncommon phenomena like mass transfer,
state transitions, and relativistic jets. Analysis of XRB gives us insights
in their formation mechanism and particularly the origin of compact objects.
Probably, their most interesting feature is the "the mass gap" (i.e., the lack of compact objects with masses ~2-5 MSun). This observation is a stringent test for compact object formation mechanism. Ultraluminous X-ray sources (ULX) are the strongest point-like X-ray sources known to date. The high energetic emission seems to be a hallmark of violent interactions between a strong gravitational field and matter. Recent works showed a strong resemblance between ULXs and XRBs suggesting that they may constitute the extreme part of their population. We know several hundred ULXs which could prove to be the marvelous laboratories of extreme processes.
Our Universe contains baryonic matter (negligible but important for us) in the form of nuclei,
which are 2-flavour symmetric (i.e., u and d flavours of quarks, known as the symmetry energy in nuclear physics).
Nevertheless, we argue that 3-flavour symmetry (i.e., u, d and s flavours of quarks) would be restored
when huge number of nuclei are compressed by gravity during a supernova, forming a gigantic macro-nuclei at last.
Different manifestations of compact stars may hint that pulsars are macro-nuclei with 3-flavour symmetry.
With the development of new observational techniques and the launch of Swift satellite,
unexpected features, such as multiple X-ray flares and significant optical rebrightenings,
which unveil the late-time activities of the central engines, have appeared in GRB afterglows.
A lot of different interpretations have been proposed to explain these complex behaviors.
The energy injection model, the two-component jet model, and the microphysics variation mechanism
are very popular in view of the fact they can explain the exceptional optical rebrightenings well.
In this report, we will introduce some special events, such as GRBs 081029, 100814A and 111209A,
which were successfully explained by the energy injection model. Especially, we will focus on GRB 100814A,
with an early-time shallow decay phase and a late-time significant rebrightening
in its optical afterglow light curve. To explain the complex multi-band afterglow emission of GRB 100814A,
we invoke a magnetar with spin evolution. We argue that the optical shallow decay phase and the X-ray plateau
are due to energy injection from the magnetar in its early spin-down stage, while
the significant optical rebrightening observed at late time naturally comes
from the spin-up process of the magnetar, which is caused by subsequent fall-back accretion.
We consider two "wonders" of hybrid stars, i.e. stars that contain a core made of quark matter.
First, we explain the existence of a very small region on the mass–radius (M-R) diagram of hybrid stars where all of the lines representing the sequences of models with different values of the bag constant B intersect. This circumstance is shown to be a consequence of the linear dependence of pressure on energy density in the quark cores of hybrid stars. Second, we show that the unusual thermodynamic properties of matter within the region of two-phase coexistence in hybrid stars result in a change of the standard condition for beginning of convection. In particular, the thermal flux transported by convection may be directed towards the stellar center. We discuss favorable circumstances leading to such an effect of "inverse" convection and its possible influence on the thermal evolution of hybrid stars. |
|
|
Design © ts@sao.ru |